
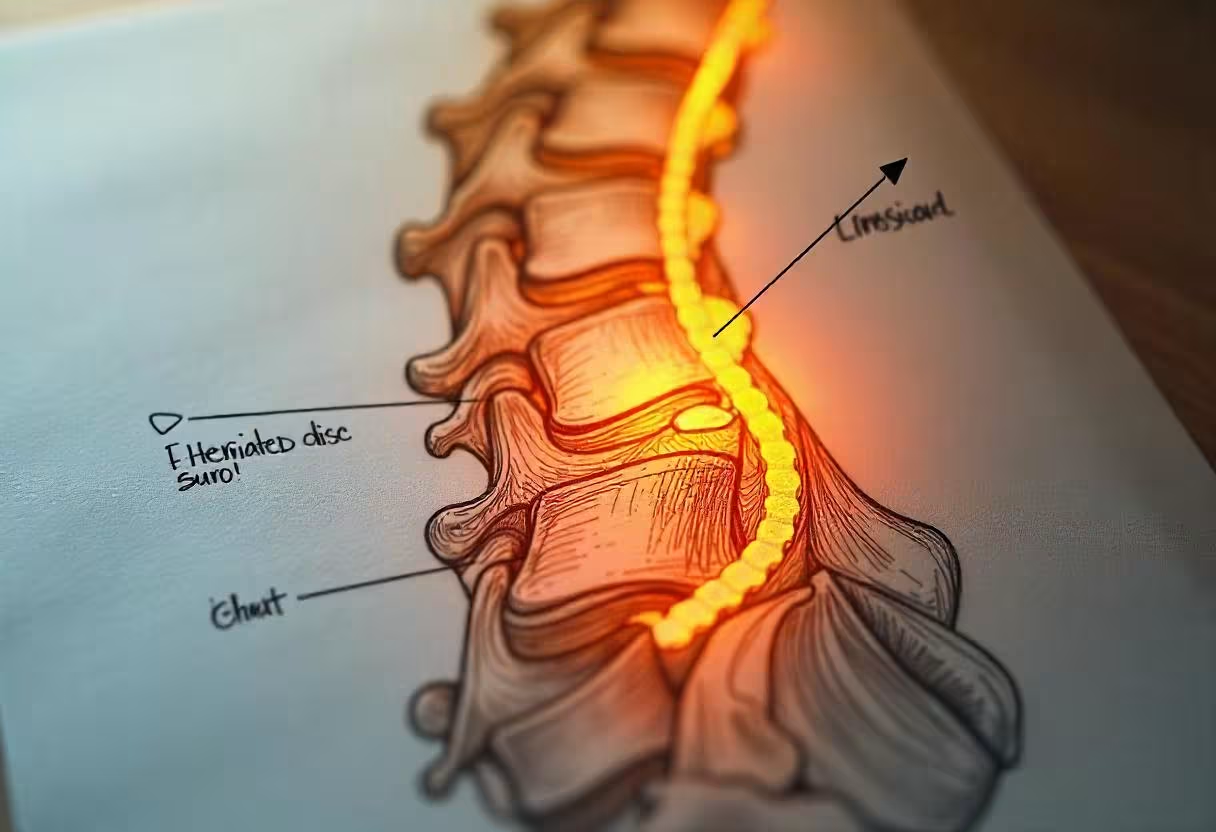
A herniated lumbar disc occurs when the soft inner material of a disc in the lower back pushes through its outer layer, compressing nearby nerves.
This condition, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, can cause significant pain and neurological symptoms.
Causes of Herniated Lumbar Disc
- Degenerative Changes: Age-related wear and tear of spinal discs.
- Injury or Trauma: Sudden impact or improper lifting techniques.
- Repetitive Strain: Prolonged activities that stress the lower back.
- Obesity: Excess weight adds pressure to the lumbar spine.
Symptoms
- Lower back pain, which may radiate to the buttocks or legs (sciatica).
- Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the legs or feet.
- Difficulty standing, walking, or bending.
- Severe cases may cause bladder or bowel dysfunction.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Assessing reflexes, strength, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to visualize the herniated disc and nerve compression.
- Nerve Studies: Electromyography (EMG) may evaluate nerve function.
Treatment Options
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications:
- NSAIDs for pain relief.
- Muscle relaxants to reduce spasms.
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises to improve mobility and reduce pressure on the nerves.
- Epidural Steroid Injections:
- Targeted injections to decrease inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Maintaining a healthy weight and practicing proper posture.
2. Surgical Treatments
For severe or persistent symptoms:
- Microdiscectomy:
- A minimally invasive procedure to remove the herniated portion of the disc.
- Laminectomy:
- Removes part of the vertebra to relieve nerve pressure.
- Spinal Fusion:
- Stabilizes the spine by fusing two vertebrae.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Post-Surgical Care:
- Pain management and gradual return to activity.
- Physical Therapy:
- Focuses on rebuilding strength and improving flexibility.
- Regular Follow-Ups:
- Ensures proper healing and addresses any complications.
Preventing Herniated Lumbar Disc
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce spinal strain.
- Use proper lifting techniques.
- Engage in regular core-strengthening exercises.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or poor posture.
