

Congenital anomalies, also known as birth defects, are structural or functional abnormalities that occur during intrauterine development.
These anomalies can affect any organ or body system and may range from mild to severe.
Common Types of Congenital Anomalies
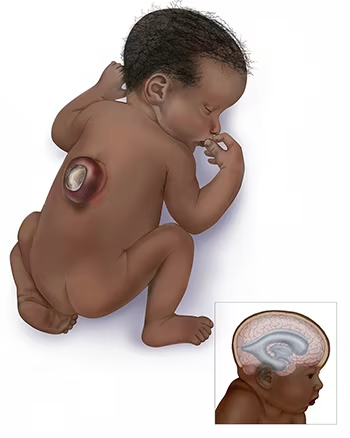
- Neural Tube Defects:
- Conditions like spina bifida and encephalocele result from improper closure of the neural tube.
- Congenital Heart Defects:
- Structural problems in the heart, such as atrial septal defect (ASD) or ventricular septal defect (VSD).
- Craniofacial Anomalies:
- Includes cleft lip, cleft palate, and craniosynostosis.
- Limb Defects:
- Malformations such as clubfoot or limb length discrepancies.
- Genetic Disorders:
- Conditions like Down syndrome or cystic fibrosis caused by chromosomal or gene abnormalities.
Causes of Congenital Anomalies
- Genetic Factors:
- Inherited mutations or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to teratogens such as alcohol, tobacco, or certain medications during pregnancy.
- Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Lack of essential nutrients like folic acid.
- Infections:
- Maternal infections such as rubella or Zika virus.
Prevention
- Folic Acid Supplementation:
- Pregnant women should take adequate folic acid before and during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
- Prenatal Care:
- Regular check-ups and imaging to monitor fetal development.
- Avoid Harmful Exposures:
- Minimize exposure to toxic substances and infections during pregnancy.
- Vaccinations:
- Ensuring maternal vaccinations are up to date, such as rubella vaccination.
Diagnosis
- Ultrasound:
- Detects structural anomalies during pregnancy.
- Amniocentesis or Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS):
- Identifies genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Newborn Screening:
- Detects metabolic or genetic conditions shortly after birth.
Treatment Options
- Surgical Interventions:
- Corrective surgeries for structural anomalies such as cleft lip or congenital heart defects.
- Therapeutic Support:
- Physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy based on the specific condition.
- Medication:
- To manage symptoms or prevent complications in metabolic or genetic disorders.
- Multidisciplinary Care:
- Collaboration between pediatricians, surgeons, geneticists, and therapists to provide comprehensive care.
