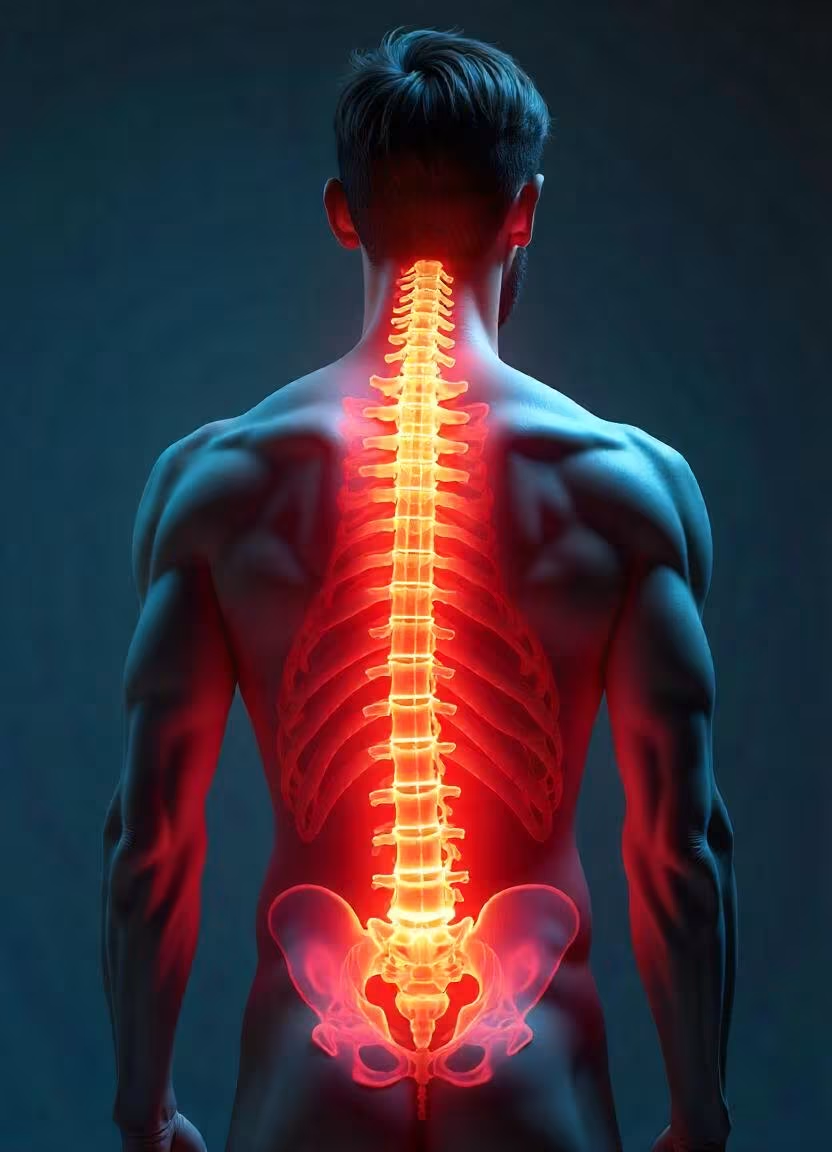
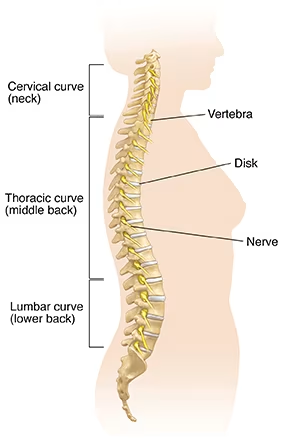

Back pain is one of the most common medical complaints, affecting people of all ages. It can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, significantly impacting daily activities and quality of life.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to manage back pain effectively.
Common Causes of Back Pain
- Muscle or Ligament Strain:
- Overstretching or tearing caused by heavy lifting or sudden movements.
- Herniated Discs:
- Occurs when the inner material of a disc pushes through its outer layer, compressing nerves.
- Arthritis:
- Inflammation in the joints, particularly osteoarthritis, can affect the spine.
- Spondylolisthesis:
- A condition where one vertebra slips over the one below it.
- Spinal Stenosis:
- Narrowing of the spinal canal, putting pressure on nerves.
- Poor Posture or Sedentary Lifestyle:
- Long hours of sitting or poor ergonomics can strain the spine.
- Injuries:
- Trauma from accidents, sports, or falls.
- Medical Conditions:
- Conditions such as scoliosis, osteoporosis, or infections.
Symptoms of Back Pain
- Dull, aching pain in the lower or upper back.
- Sharp or stabbing pain radiating down the legs (sciatica).
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion.
- Muscle spasms.
- Weakness or numbness in the legs.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Identifying areas of tenderness, flexibility, and muscle strength.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to detect structural problems.
- Electromyography (EMG): Tests nerve function and identifies nerve compression.
Treatment Options
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen).
- Muscle relaxants or prescription medications for severe pain.
- Physical Therapy:
- Strengthening exercises, stretching, and posture correction.
- Chiropractic Care:
- Spinal manipulation to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Epidural Steroid Injections:
- Reduces inflammation around nerve roots.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight management, improved ergonomics, and regular exercise.
2. Surgical Treatments
- Discectomy:
- Removes part of a herniated disc to relieve nerve pressure.
- Spinal Fusion:
- Joins two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
- Laminectomy:
- Removes a portion of the vertebra to relieve nerve compression.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
· Exercise Programs:
o Focus on flexibility, core strength, and overall fitness.
· Pain Management:
o Includes medications, heat/ice therapy, and alternative methods like acupuncture.
· Assistive Devices:
o Braces or orthotics to provide support during recovery.
Preventing Back Pain
- Maintain proper posture.
- Use ergonomic furniture and equipment.
- Stay physically active with regular exercise.
- Avoid heavy lifting or use proper techniques when lifting.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the spine.
